GREEN EDGE DATA CENTER DEPLOYMENT
- K. Manohar Raja, Executive Director,RailTel
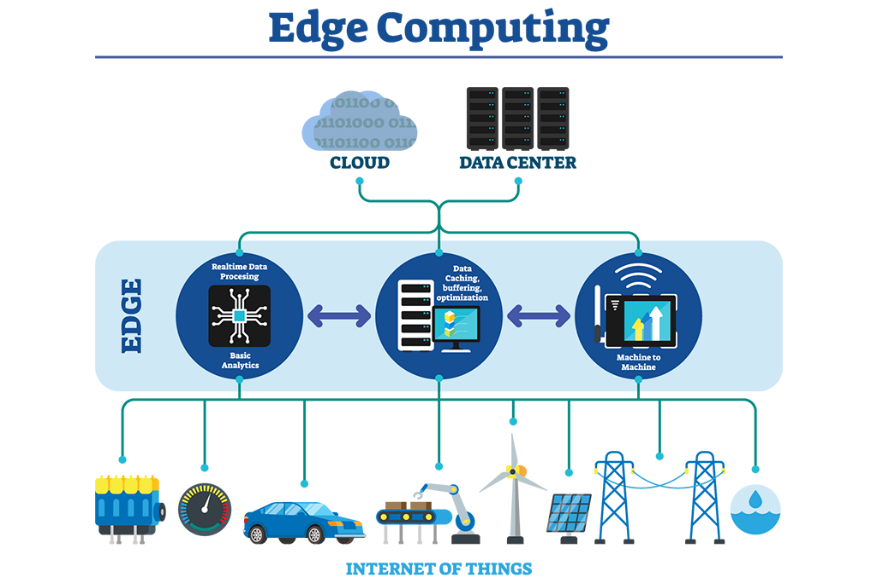
Edge computing is the delivery of computing solutions (applications and services) at the logical extremes of the network edge, closer to the end-user. For example, vast amounts of IoT or machine-to-machine data can be processed by edge computing and only the most relevant and valuable information is sent to a centralized data center, thus saving the scarce network resources.
Edge computing provides services in a context of reduced network costs, application latency and thereby provides better customer experience.
Centralized data centres or hyper scale cloud provider models deliver large-scale resources and gain advantage via economies of scale. Parties share capacity, critical infrastructure, applications, cloud services, staff and peering in one location.
This model will be enhanced by adding EDCs to support application requirements that cannot be supported over long network links from centralized DCs. This will overcome barriers such as communication latency and long-distance transmissions costs and will make it possible to support IoT and many of the next generation latency sensitive applications. It is important to keep in mind that EDCs relocate the geographic extent of the network and computing infrastructure; it is complementary to the current computing design and network infrastructure. The edge and the core form a holistic infrastructure where the needs and requirements of applications including latency, performance, security and cost determine the location of the resources supporting them.
The Importance of Latency
Today, many modern network functionalities, such as content streaming and interactive entertainment, are already constricted by latency, more than the bandwidth. Next generation applications, such as connected cars, AR/VR and drone technology require even higher constraints on application latency. High-reliability, low-latency networks rely on the ability of the network to deliver consistent low latency and high capacity. Many applications, such as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) based on Industry 4.0 standard, Rolling stock predictive and preventive maintenance, autonomous cars, medical technology, drones and various public safety systems, rely on guaranteed response times.
Data transmission latency increases as the network distances increase. Long-distance transmissions inherently have too much latency to support many of the emerging applications.
Edge Data Center Considerations
Critical infrastructure services play a foundational role in the development and delivery of any data center. EDCs are required to support a wide variety of distributed services with appropriate availability and investment costs, thus requiring new design and operating procedures.
a) Location
Traditional data center sites are selected in large part based on geographical considerations, including power availability and cost, customer demand, real-estate price, and physical and security risk factors. However, for the edge data center, location will also be dictated by the latency requirements of the service it supports and access to network resources.
Edge Data Center Location Examples include:
- A cabinet located on a street corner or near other utility equipment
- Re-utilization of existing macro cell site shelters
- Placement of new shelters / cabinets at macro-cell sites
- Co-location within Central Offices
- In buildings / Smart Buildings
- In factories/PUs to support Industrial IoT
- Behind or co-located with gas stations, drugstores and other businesses
As a result, EDC site selection will need to be adapted to include locations with less than ideal climate profiles, population density (urban), and macro operational risk factors, including proximity to flood zones, fault lines, and airports. EDC location criteria must also satisfy security and availability requirements through new and innovative network and facility designs.
b) Operational Risk Factors and Considerations
Availability and Mean time to repair (MTTR) are critical factors in EDCs. Given that EDC sites are remote and unmanned, strategies to minimize service outages and excessive operating expense are important design criteria.
c) Environmental Operating Considerations
Traditional data center operators tightly control the data center operating environment, whereas an EDC might be small, unmanned, and located in the desert among oil pipes – obviously challenged to provide the significantly controlled, monitored and restricted operating environment of the traditional data center. Modern connectivity, storage, and compute hardware are routinely able to operate in adverse conditions. Relaxing the operating environment restrictions greatly reduces the requirement for mechanical cooling, lowering power requirements for cooling.
Smart Row Solution
RailTel has deployed Smart Row Solution for Green Edge Data Centers at, Bengaluru, Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkatta and Secunderabad. The smart row solution has two racks at each end provided with Precision AC units and does not require room air conditioners. The server racks have extended plenum in the front and the rear which acts as cold & hot aisle respectively to optimise the cooling and significantly reduce energy consumption thus making it a Green Edge DC. The system is provided with fire suppression system, smoke and flame detection, CCTV camera and IoT for centralised management. In case of prolonged power failure and at a certain temperature the doors of the rack open up automatically to allow ambient cooling. Thus provides sufficient time for the maintenance teams to reach the site.
The system uses intelligent power management for IT load. All the green edge DC are managed centrally by RailTel from Secundrabad. The Edge Datacentres are connected on High Speed secure MPLS network to the Central Data Center and managed centrally. The Smart Solutions is a pre-engineered, Make in India, factory fabricated solution deployed with IoT that combines the best IT infrastructure systems/sub-systems under one roof.
- Dedicated Server Racks.
- Built-in cooling systems with redundancy in operation.
- UPS systems that ensure 100% uptime.
- Highly advanced Monitoring & control systems.
- Effective Power Management & distribution.
- Cable Management
- Access Control to the entire system.
- Fire Suppression systems.

The Smart Row infrastructure utilizes data center best practices and technologies to achieve a unique set of benefits.
- 1) Maximizes the return temperature at the Cooling units to improve capacity and efficiency.
- 2) Matches cooling capacity with IT load
- 3) Utilizes cooling design that reduce energy consumption
- 4) Uses power management systems that optimize availability and efficiency
- 5) Features a design that enhances flexibility using scalable architectures that minimize footprint.
- 6) Utilizes real-time infrastructure optimization to provision resources faster, increase efficiency and reduce stranded capacity.
- 7) Leverages the availability of in-market data center design expertise and technical assistance.
- 1) Reduce annual energy costs upto 27% through high-efficiency power, dedicated cooling and management technologies and containment
- 2) Significantly reduces the cost of room upgrades or modifications. Saves upto 28% on room upgrades compared to upgrading a room as a conventional data center.
- 3) Integrated fire suppression – saves 66% over room-based systems by avoiding room upgrades.
- 4) Lower preventive maintenance costs than a traditional data center in some cases by as much as 33%
- 5) Reduces cooling power usage through contained airflow, digital scroll compressor technology and controls. Instead of cooling an entire room as in conventional designs, the Smart Row infrastructure cools only the rack space.
- 6) Reduces time and cost of implementation.
- 7) Optimize space efficiency through an integrated system.
- 8) Increase physical security and equipment protection with lockable cabinets and access alerts
- 9) Increases IT control and productivity by offering integrated data center infrastructure management technologies that make moves/adds/changes easier and support remote monitoring and management.
- 10) Optimizes use of space. The Smart-Row DCR unit has a minimum footprint of only 39 square feet and can fit in a room as small as 10ft. X 19ft. (w x d) (3 Rack Primary Configuration).
- 11) Centralized Monitoring Software allows centralized, real-time monitoring for any Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) device that supports a network interface such as access, door open close, fire suppression system cooling UPS systems etc, Triggers event actions such as email alerts or notifications, Allows more runtime to most critical systems by sending shutdown commands to user-defined non-critical systems. Advanced graphics and user-friendly navigation enhance usability.
Benefits of Smart Row infrastructure solution
Conclusion
Developments in the IT industries may surpass the perception of many industries in this new digitized generation. The ever demanding, data-addicted, customers requiring faster connectivity speeds have the IT industry in awe and wondering how to satisfy them..
With increase in the level of automation in all areas, the need for low latency in data transmission will increase , leading to shifting the compute power near the user and requirements of EDCs. The Edge does not stand alone but is connected forming an interoperable fabric extending from device to core to cloud. The future will have optimal mix of both Centralised and Edge data centres
